Patch Tuesday, October 2025 ‘End of 10’ Edition
Microsoft today released software updates to plug a whopping 172 security holes in its Windows operating systems, including at least three vulnerabilities that are already being actively exploited. October's Patch Tuesday also marks the final month that Microsoft will ship security updates for Windows 10 systems. If you're running a Windows 10 PC and you're unable or unwilling to migrate to Windows 11, read on for other options.
Microsoft today released software updates to plug a whopping 172 security holes in its Windows operating systems, including at least two vulnerabilities that are already being actively exploited. October’s Patch Tuesday also marks the final month that Microsoft will ship security updates for Windows 10 systems. If you’re running a Windows 10 PC and you’re unable or unwilling to migrate to Windows 11, read on for other options.

The first zero-day bug addressed this month (CVE-2025-24990) involves a third-party modem driver called Agere Modem that’s been bundled with Windows for the past two decades. Microsoft responded to active attacks on this flaw by completely removing the vulnerable driver from Windows.
The other zero-day is CVE-2025-59230, an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Windows Remote Access Connection Manager (also known as RasMan), a service used to manage remote network connections through virtual private networks (VPNs) and dial-up networks.
“While RasMan is a frequent flyer on Patch Tuesday, appearing more than 20 times since January 2022, this is the first time we’ve seen it exploited in the wild as a zero day,” said Satnam Narang, senior staff research engineer at Tenable.
Narang notes that Microsoft Office users should also take note of CVE-2025-59227 and CVE-2025-59234, a pair of remote code execution bugs that take advantage of “Preview Pane,” meaning that the target doesn’t even need to open the file for exploitation to occur. To execute these flaws, an attacker would social engineer a target into previewing an email with a malicious Microsoft Office document.
Speaking of Office, Microsoft quietly announced this week that Microsoft Word will now automatically save documents to OneDrive, Microsoft’s cloud platform. Users who are uncomfortable saving all of their documents to Microsoft’s cloud can change this in Word’s settings; ZDNet has a useful how-to on disabling this feature.
Kev Breen, senior director of threat research at Immersive, called attention to CVE-2025-59287, a critical remote code execution bug in the Windows Server Update Service (WSUS) — the very same Windows service responsible for downloading security patches for Windows Server versions. Microsoft says there are no signs this weakness is being exploited yet. But with a threat score of 9.8 out of possible 10 and marked “exploitation more likely,” CVE-2025-59287 can be exploited without authentication and is an easy “patch now” candidate.
“Microsoft provides limited information, stating that an unauthenticated attacker with network access can send untrusted data to the WSUS server, resulting in deserialization and code execution,” Breen wrote. “As WSUS is a trusted Windows service that is designed to update privileged files across the file system, an attacker would have free rein over the operating system and could potentially bypass some EDR detections that ignore or exclude the WSUS service.”
For more on other fixes from Redmond today, check out the SANS Internet Storm Center monthly roundup, which indexes all of the updates by severity and urgency.
Windows 10 isn’t the only Microsoft OS that is reaching end-of-life today; Exchange Server 2016, Exchange Server 2019, Skype for Business 2016, Windows 11 IoT Enterprise Version 22H2, and Outlook 2016 are some of the other products that Microsoft is sunsetting today.
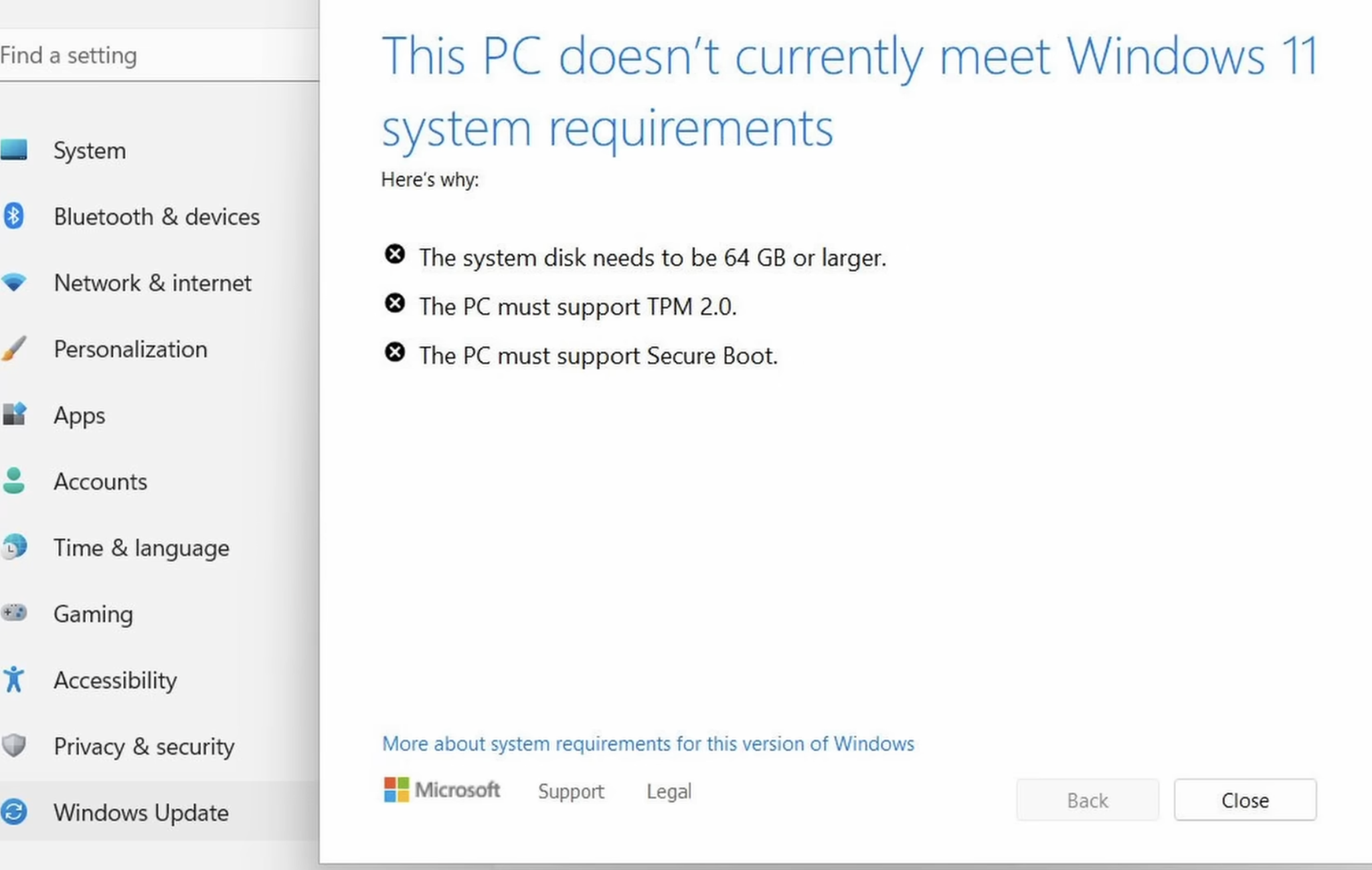
If you’re running any Windows 10 systems, you’ve probably already determined whether your PC meets the technical hardware specs recommended for the Windows 11 OS. If you’re reluctant or unable to migrate a Windows 10 system to Windows 11, there are alternatives to simply continuing to use Windows 10 without ongoing security updates.
One option is to pay for another year’s worth of security updates through Microsoft’s Extended Security Updates (ESU) program. The cost is just $30 if you don’t have a Microsoft account, and apparently free if you register the PC to a Microsoft account. This video breakdown from Ask Your Computer Guy does a good job of walking Windows 10 users through this process. Microsoft emphasizes that ESU enrollment does not provide other types of fixes, feature improvements or product enhancements. It also does not come with technical support.
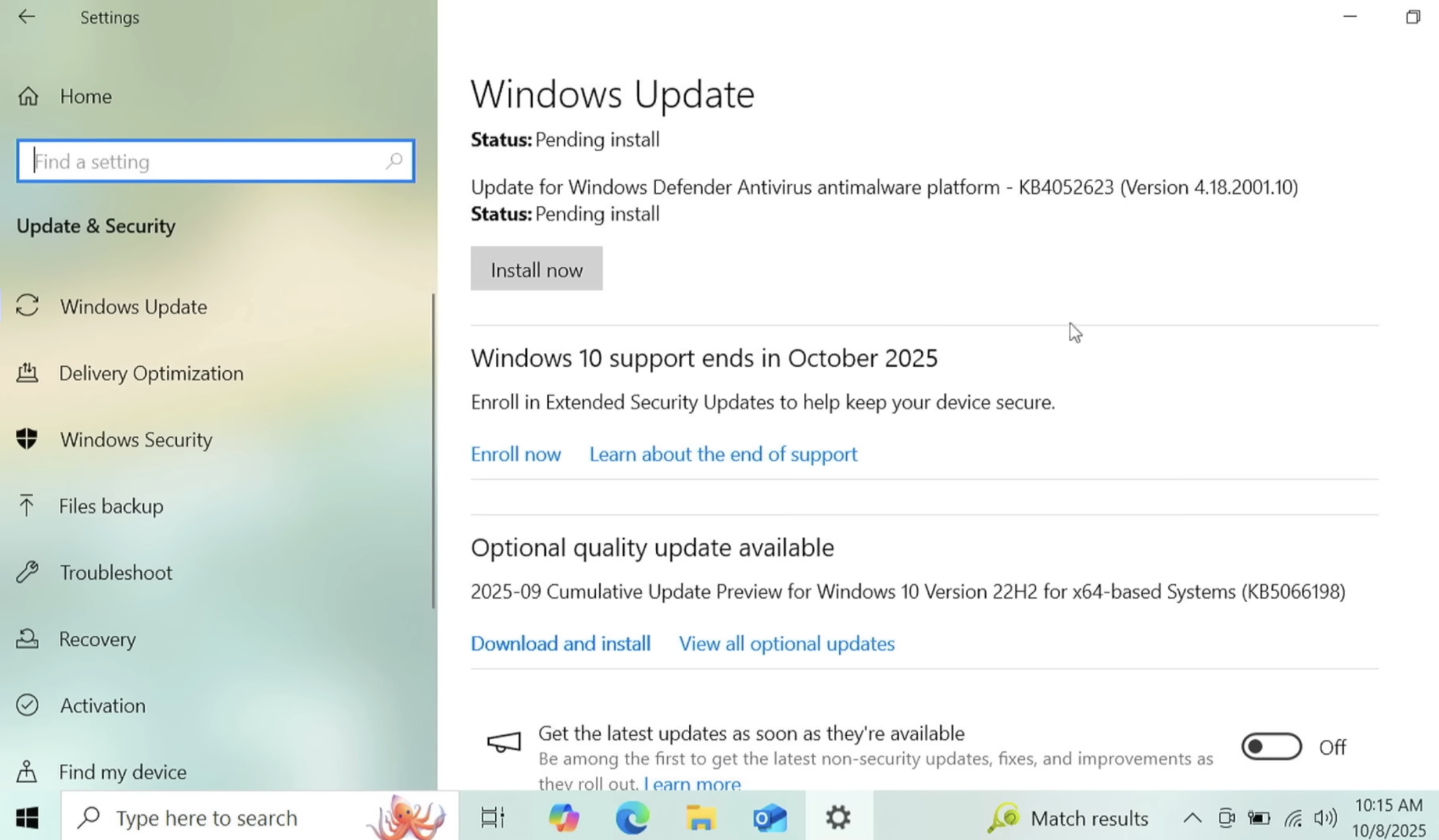
If your Windows 10 system is associated with a Microsoft account and signed in when you visit Windows Update, you should see an option to enroll in extended updates. Image: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SZH7MlvOoPM
Windows 10 users also have the option of installing some flavor of Linux instead. Anyone seriously considering this option should check out the website endof10.org, which includes a plethora of tips and a DIY installation guide.
Linux Mint is a great option for Linux newbies. Like most modern Linux versions, Mint will run on anything with a 64-bit CPU that has at least 2GB of memory, although 4GB is recommended. In other words, it will run on almost any computer produced in the last decade.
Linux Mint also is likely to be the most intuitive interface for regular Windows users, and it is largely configurable without any fuss at the text-only command-line prompt. Mint and other flavors of Linux come with LibreOffice, which is an open source suite of tools that includes applications similar to Microsoft Office, and it can open, edit and save documents as Microsoft Office files.
If you’d prefer to give Linux a test drive before installing it on a Windows PC, you can always just download it to a removable USB drive. From there, reboot the computer (with the removable drive plugged in) and select the option at startup to run the operating system from the external USB drive. If you don’t see an option for that after restarting, try restarting again and hitting the F8 button, which should open a list of bootable drives. Here’s a fairly thorough tutorial that walks through exactly how to do all this.
And if this is your first time trying out Linux, relax and have fun: The nice thing about a “live” version of Linux (as it’s called when the operating system is run from a removable drive such as a CD or a USB stick) is that none of your changes persist after a reboot. Even if you somehow manage to break something, a restart will return the system back to its original state.
As ever, if you experience any difficulties during or after applying this month’s batch of patches, please leave a note about it in the comments below.
Published: 2025-10-14T22:57:38
Privacy | Terms of Use | Contact Us
